Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence at UCCS
The university is actively assessing and exploring the impact of Artificial intelligence (AI) on teaching and learning, research and scholarship, administrative processes, and other functions. Although AI is not new and has been a part of our lives for decades, its potential usefulness is transforming the way we think about our daily work.
AI is a catch-all term for tech that helps machines do things that usually need human smarts, like thinking, problem-solving, learning from experience, and adapting to new situations. It breaks down into a few main areas:
- Machine Learning (ML): ML involves computers learning from data and improving their performance over time. They can identify patterns, make predictions, and sort information based on past observations. For instance, machine learning algorithms help identify spam emails by analyzing patterns.
- Deep Learning (DL): DL uses networks of artificial "neurons" to understand complex data relationships. It excels at tasks like recognizing images, understanding human language, and even creating human-like speech. These models can, as an example, can assist doctors in diagnosing medical conditions by analyzing medical images.
- Generative AI: This area of AI focuses on creating new content, such as images, text or music. A good example is DALL-E, which can create unique images from descriptions you give it.
On campus, our information technology and security teams have been exploring AI's potential and have approved the following AI tools for university use:
- ChatGPT EDU (General availability on 3/31/2026)
- Microsoft Copilot for the Web (formerly known as Bing chat Enterprise): Microsoft Copilot lets you chat with an AI agent within your Edge or Bing browser that can answer your questions, generate content, or help you with tasks using public online data. Think of it as a smart and friendly chatbot that can talk to you about anything you want.
- Copilot for Microsoft 365: Copilot for Microsoft 365 is an AI-powered assistant designed to enhance productivity and streamline workflows within the Microsoft 365 suite. By leveraging advanced AI and machine learning technologies, Copilot helps users quickly generate content, analyze data, summarize documents, learn new skills, and write code.
- Zoom AI Companion: Zoom AI Companion is an intelligent assistant integrated into the Zoom platform, designed to enhance virtual meetings and collaboration. This AI-powered tool can help staff and faculty by generating meeting summaries, transcribing conversations, and highlighting key points in real time. It can also provide actionable insights, suggest next steps, and assist with scheduling and follow-ups.
- Adobe Firefly: Adobe Firefly is a suite of generative AI tools integrated into Adobe's Creative Cloud, designed to enhance creativity and streamline the creative process. Firefly leverages advanced AI to generate images, graphics, and other visual content from textual descriptions, allowing users to quickly and easily bring their creative visions to life.
- BoodleBox: The AI platform where faculty and students can affordably access top AI models, responsibly while collaborating with AI and each other. No-cost accounts available to UCCS faculty/staff/students. To access a free account, sign up on their platform and send an email to helpdesk@uccs.edu to get started.
Best Practices When Using AI
- Gain a basic understanding of how AI works, including its capabilities and limitations, with the available tools approved for use at the university.
- Clearly define what you want to achieve with AI. Whether it’s automating tasks, improving decision-making, or enhancing user experiences, having clear objectives will guide your AI implementation.
- The use of AI should be clearly documented and disclosed. Ensure to cite your AI usage clearly if incorporating written prompts.
- Always evaluate results as responses may not always be accurate. Verify information using credible sources to ensure accuracy.
- Be cautious about bias detection; a fairness assessment can help ensure equitable results. Evaluate whether an AI model treats all individuals equitably by ensuring data quality, defining the fairness criteria and identifying protected attributes such as race or gender, for example.
- Prioritize ethical guidelines, fairness, openness, and privacy laws.
- Ensuring data protection is our top priority. These tools are currently approved for use with public and confidential data, as defined in the university’s data classification system. Do not input highly confidential data into these AI tools.
Guidelines for Safely Using AI
Data Privacy
These AI tools are currently approved only for use with public and confidential data. The University of Colorado has adopted data classification types including highly confidential information, confidential information and public information. Review the CU Data Classification Table for more information about data types. Be cautious when using AI tools, ensuring that personal, sensitive and university data are not uploaded or shared with unvetted AI systems, as they may not be secure. How an AI tool or assistant processes and uses the data that is input into it is a key factor in determining its security. Refer to our AI Tool Comparison webpage for more information.
In addition to using university approved AI tools with public or confidential data, all users must follow and abide by university policy, and relevant state and federal law regarding protecting data and information systems, including but not limited to HIPAA, FERPA, GLBA, GDPR, FISMA (NIST 800-53r5), University HIPAA Compliance Policy, Responsible Computing Policy 700-002, and Administrative Policy Standard 6005 Information Security Program.
Please note: For Microsoft AI tools, though Microsoft assures that your data and university data won’t be used to train their artificial bot, it is still advisable to exercise caution. When using Copilot Chat, be sure you are logged in to your university account and confirm that the green "Protected" shield is visible in the prompt area. Additional information about securely using AI are available. Visit the OIT resource pages: Microsoft Copilot products, and Zoom AI Companion features.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Security Compliance
CU is in the process of establishing guidelines and compliance requirements for using AI — with the complexity of this technology, it may take some time. And without proper security controls, AI technology can become susceptible to privacy, confidentiality, and security threats. Cybercriminals could inject malicious data or images into a machine learning model to deliberately attack the integrity of the data. Data uploaded into AI technology could remain there permanently, circumventing appropriate university protections and security controls.
As we collaborate with cross campus experts to establish AI guidelines for UCCS employees, our team recommends resources from the following entities when researching the use of AI.
• OWASP AI Security and Privacy Guide
• Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency News Blog
• National Institute of Standards and Technology - Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework
Be sure to avoid uploading or sharing university data into unvetted AI systems as they are not secure. Request a OIT Solutions Request for assistance vetting AI prior to acquiring a technology, particularly if the AI is intended for clinical purposes or will use highly confidential data such as FERPA or HIPAA data.
How to Use AI in Your Work
Faculty and staff can harness the power of AI in various ways to streamline processes and improve productivity. One of the most effective ways to use these approved Generative AI tools is to create clear and concise prompts, called prompt engineering. Prompt engineering involves crafting effective input prompts to guide the model’s responses.
Decide what you want to ask and provide context to why you're asking. Instead of asking "Tell me about AI" you can ask, "What are the key applications of AI in healthcare and how are they improving patient outcomes." Or you could pick a topic and ask for step-by-step explanations, "What are the top five things I should know when managing a large project? and What is agile project management and how does it differ from waterfall?" Providing context and asking if more information is needed will provide better results.
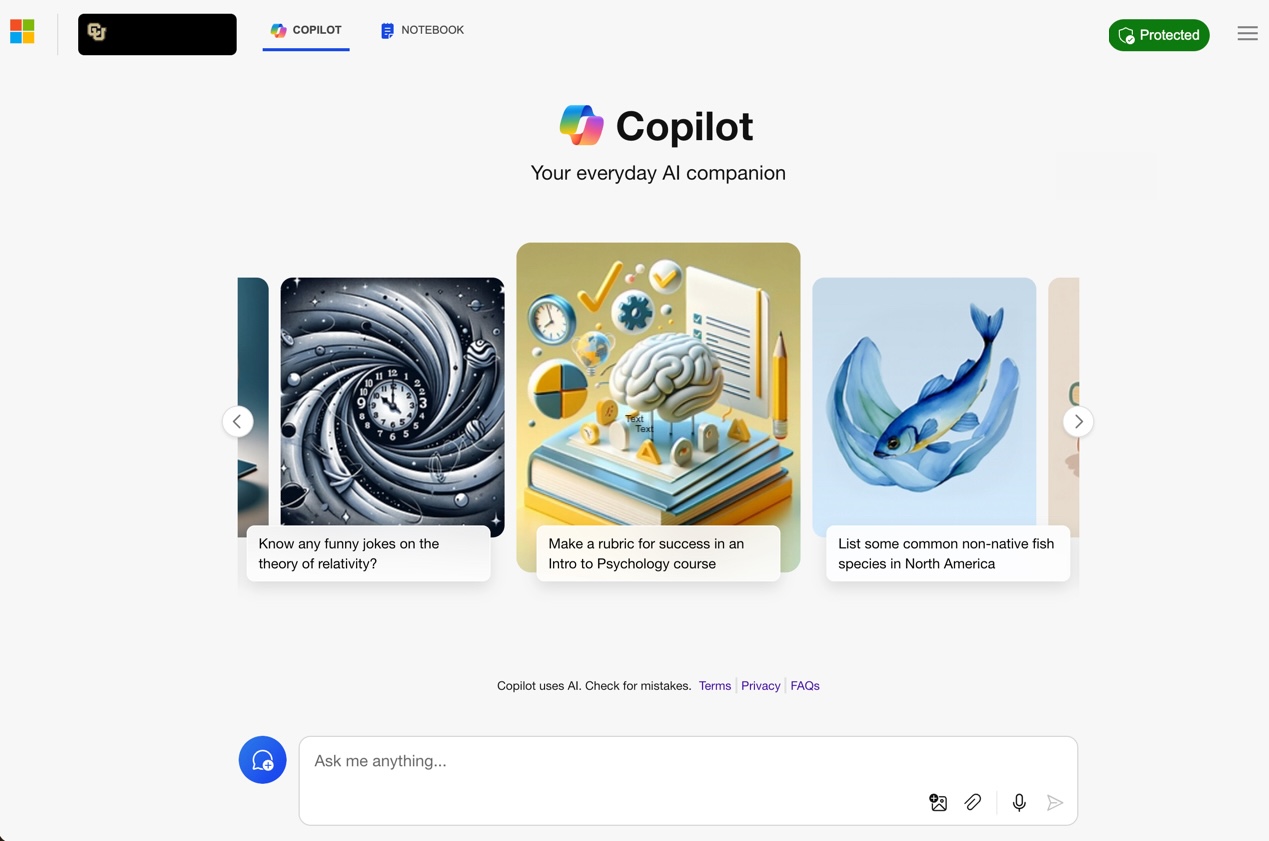
When using Copilot Chat, the start image where you will input the prompt will look like the following:
DALL-E has been integrated into Copilot, enhancing its capabilities with advanced image generation. This integration empowers Copilot users to create custom visuals, streamlining content creation for academic and administrative purposes. Prompt engineering is important with asking AI to create a DALL-E image as well.
For example, the following specific instructions were used to generate the four sample images below: Create a highly detailed, realistic image of a modern research campus. Include state-of-the-art buildings with large glass windows, a central plaza with green spaces and benches, students walking and discussing projects, and researchers in lab coats working in a high-tech laboratory visible through the windows. The scene should have a vibrant, sunny atmosphere.